8 Tips To Teach Active Listening Skills for Students
Active listening is a vital communication attribute that implies giving all attention, comprehending the speaker’s message, and responding thoughtfully. Unlike passive hearing, which requires focus, empathy, and engagement, active listening is integral for building a good and healthy relationship, resolving conflict, and ensuring better collaboration. Let’s discover what active listening skills mean, their benefits for a student, and some easy techniques to master them.
What Are Active Listening Skills?
Active listening abilities require concentrating fully on the person speaking, comprehending their message, and replying with consideration. In contrast to passive hearing, active listening guarantees that the listener remains engaged and empathetic during the discussion.
Key elements include maintaining eye contact, asking clarifying questions, and paraphrasing the speaker’s words. This technique will improve communication, build respect, and make stronger relationships in both academic and personal life.
Benefits of Active Listening Skills for Students
Mastering active listening offers numerous advantages, especially for students navigating academic and social environments. Here’s how it impacts various aspects of their lives.
Enhancing Communication & Social Relationships
Active listening helps improve communication by assisting students to make better connections with peers and mentors. They build up trust and understanding, a foundation of meaningful relationships, by being all ears and responding thoughtfully. For instance, when students listen during group discussions, they create an inclusive environment where everyone can voice their thoughts.
Boosting Academic Understanding
Active listening helps students grasp complex topics more effectively in an academic setting. Paying attention in class enables them to process key details, ask thoughtful questions, and clarify doubts. As a result, they retain information better and perform well in exams and projects. Teachers also appreciate engaged students, leading to more personalized support and guidance.
Collaborating and Resolving Conflicts
Whether working on group projects or resolving disagreements, active listening helps students find common ground. By fully understanding each perspective, they can propose fair and constructive solutions.

Building Self-Awareness
Reflective listening fosters self-awareness, enabling students to evaluate their behavior and identify areas for improvement. By listening to feedback from teachers or peers, they develop critical thinking and better decision-making skills.
Identifying and Anticipating Problems
Students with active listening skills can detect subtle cues in conversations, such as a peer’s frustration or a teacher’s concern, enabling them to identify potential challenges early on. Whether it’s following detailed instructions or understanding feedback, they are capable of addressing problems before they arise. This proactive approach enhances their problem-solving abilities and prepares them for future responsibilities.
8 Practices to Teach Students Active Listening Skills
Teaching active listening requires practical and engaging methods that students can incorporate into daily interactions. Below are eight effective practices:
Set Explicit Guidelines
Define behaviors in concrete terms: for example, maintain eye contact, do not interrupt, and give reflective feedback. The guidelines provide a firm base, set expectations, and create an environment for respectful communication.
Model Active Listening
Teachers and parents can model attentive behaviors during conversations by responding with questions or rewording points to show comprehension of the delivered messages. For example, during discussions in the classroom, a listening teacher who responds thoughtfully makes students interested in doing the same with their peers.
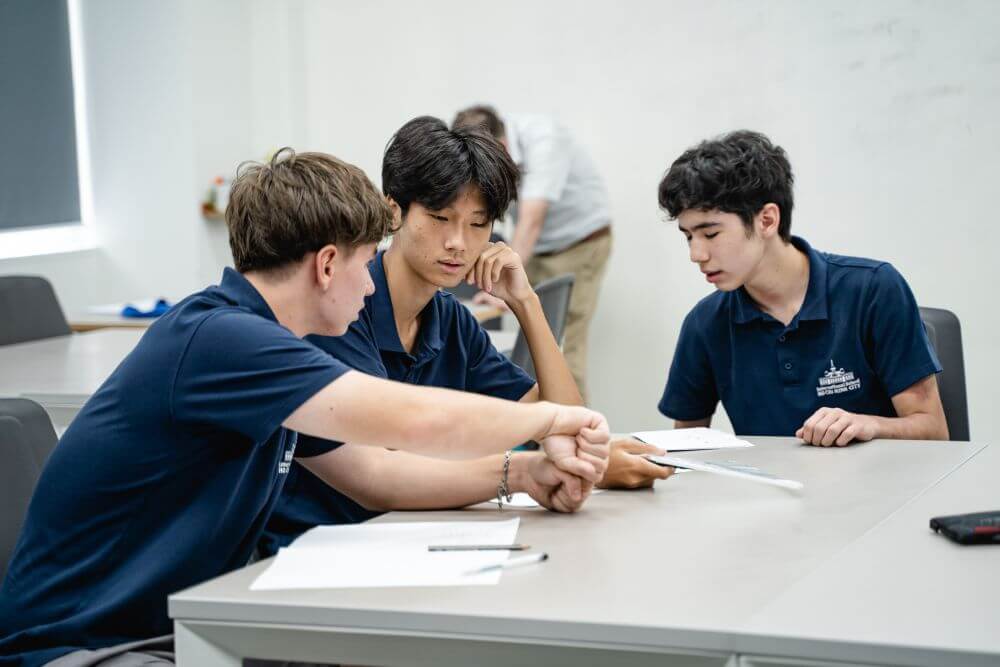
Establish Peer Accountability
Pairing students to practice active listening in structured conversations, such as discussing an assigned topic, encourages mutual feedback. For example, one student can narrate a story while the other listens, paraphrases, and asks questions. They become more mindful of their behavior by asking students to evaluate each other’s listening skills in collaborative tasks.
Practice Paraphrase
After hearing a statement, students paraphrase it in their own words to ensure that they have processed and understood the information correctly. Teachers can integrate this practice during lessons by asking students to rephrase instructions or summarize a peer’s comment, encouraging active engagement with content.

Encourage Students’ Regular Reflection
Incorporate moments for students to reflect on their listening habits and identify areas where they can improve. Teachers can dedicate time for students to journal their listening experiences, noting challenges and successes. Over time, students develop a deeper understanding of their listening strengths and areas needing attention.
Open-Ended Questions
Prompt students with questions that require thoughtful answers, such as “Why do you think this solution works?” can stimulate meaningful conversations and critical thinking. This technique can also enhance classroom discussions, making students feel heard and valued.
Make Eye Contact
Eye contact is an important nonverbal cue that signifies attentiveness and respect. Teachers should encourage students to maintain appropriate eye contact during conversations, such as presentations or peer interactions, to strengthen the connection between speaker and listener and sustain engagement.
Use Positive Body Language
Positive gestures, such as nodding, smiling, or leaning forward, indicate they are listening and valuing what speakers say. Teaching students to incorporate these non-verbal cues into their interactions can make their listening skills more effective and empathetic.
At ISHCMC, active listening techniques are in use through group projects, peer feedback sessions, and discussions that make students engage in interactive ways, solve problems, and create meaningful connections—a necessary skill for success both at school and beyond.
Active Listening: A Core Skill Nurtured at ISHCMC!
Active listening is a vital skill that shapes a student’s academic and personal journey. By enhancing communication, fostering collaboration, and boosting self-awareness, students become more effective learners and empathetic individuals.
ISHCMC’s approach to learning helps students develop communication skills, enabling them to be better at listening, interpreting, and speaking. At ISHCMC, learners are equipped to set themselves up for success in an ever-connected world through interactive activities, peer collaborations, and reflective exercises.